Disorders of the…Integumentary System
The first thing a clinician sees is the skin, and so the examination of the skin should be part of any thorough physical examination. Most skin disorders are relatively benign, but a few, including melanomas, can be fatal if untreated. A couple of the more noticeable disorders, albinism and vitiligo, affect the appearance of the skin and its accessory organs. Although neither is fatal, it would be hard to claim that they are benign, at least to the individuals so afflicted.
Bạn đang xem: Anatomy & Physiology
Xem thêm : How to become an infertility counsellor
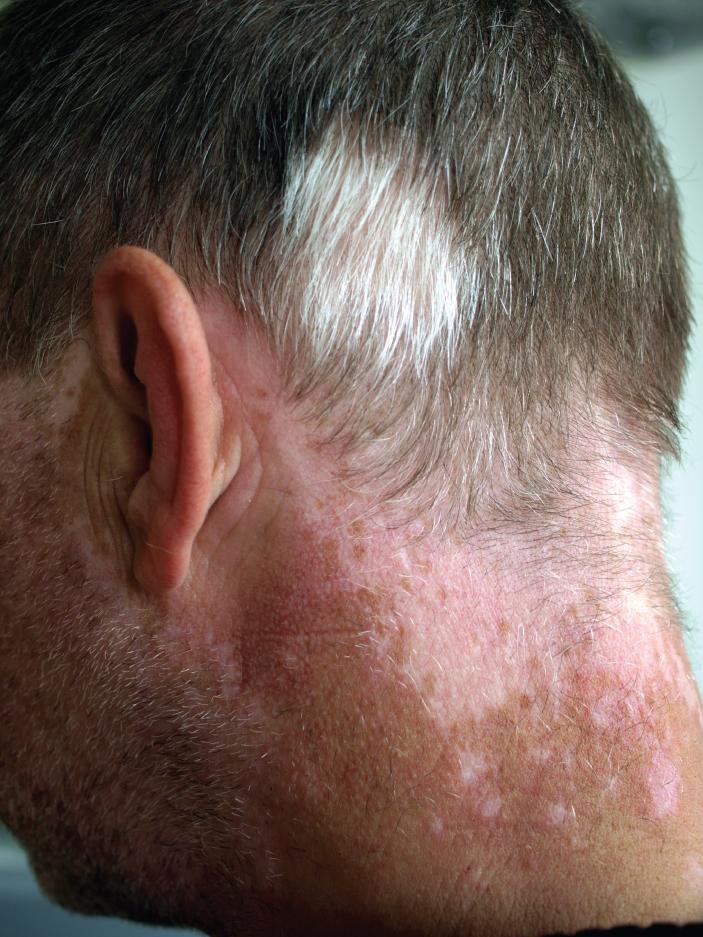
Albinism is a genetic disorder that affects (completely or partially) the coloring of skin, hair, and eyes. The defect is primarily due to the inability of melanocytes to produce melanin. Individuals with albinism tend to appear white or very pale due to the lack of melanin in their skin and hair. Recall that melanin helps protect the skin from the harmful effects of UV radiation. Individuals with albinism tend to need more protection from UV radiation, as they are more prone to sunburns and skin cancer. They also tend to be more sensitive to light and have vision problems due to the lack of pigmentation on the retinal wall. Treatment of this disorder usually involves addressing the symptoms, such as limiting UV light exposure to the skin and eyes. In vitiligo, the melanocytes in certain areas lose their ability to produce melanin, possibly due to an autoimmune reaction. This leads to a loss of color in patches (Figure 5.1.9). Neither albinism nor vitiligo directly affects the lifespan of an individual.
Other changes in the appearance of skin coloration can be indicative of diseases associated with other body systems. Liver disease or liver cancer can cause the accumulation of bile and the yellow pigment bilirubin, leading to the skin appearing yellow or jaundiced (jaune is the French word for “yellow”). Tumors of the pituitary gland can result in the secretion of large amounts of melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH), which results in a darkening of the skin. Similarly, Addison’s disease can stimulate the release of excess amounts of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), which can give the skin a deep bronze color. A sudden drop in oxygenation can affect skin color, causing the skin to initially turn ashen (white). With a prolonged reduction in oxygen levels, dark red deoxyhemoglobin becomes dominant in the blood, making the skin appear blue, a condition referred to as cyanosis (kyanos is the Greek word for “blue”). This happens when the oxygen supply is restricted, as when someone is experiencing difficulty in breathing because of asthma or a heart attack. However, in these cases the effect on skin color has nothing do with the skin’s pigmentation.
Nguồn: https://blogtinhoc.edu.vn
Danh mục: Info








