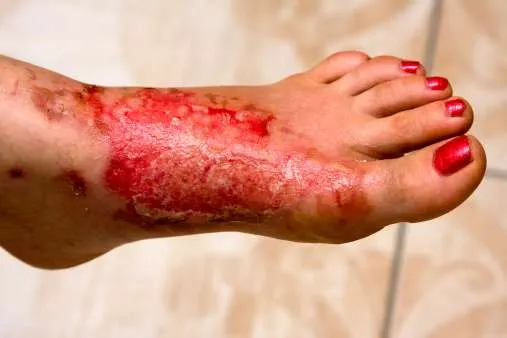
Most people have likely experienced a light burn or scald. These usually come from heated objects, sparks from outlets, and even smartphones charging for too long.
Then, some have experienced direct injuries from fires. The higher the temperatures, the worse the damage.
Bạn đang xem: Reactions to Extreme Burns and Extreme Heat
How high or hot must the temperature be to start introducing radical and intense injuries? How hot does it need to be for skin and fat to melt off? What adverse effects do high temperatures bring about?
Read on as we examine the effects of extreme burns and extreme heat. Let’s start by reviewing burns closely.
What Are Burns?
There are generally three types of burns that people experience: scalds, contact, and inhalation.
A scald is when a hot liquid or steam has damaged the skin. A contact burn is a skin burn that directly contacts a heat source, like a stovetop. Lastly, an inhalation burn is when hot gases have been inhaled and damage the lungs.
These burns are further categorised into degrees and types.
Degrees
These can be further broken down into first-, second-, and third-degree burns.
A first-degree burn only affects the epidermis, the outermost layer of skin. It is similar to a sunburn and will likely heal within a week.
A second-degree burn will damage the epidermis and the next layer down, which is the dermis. This kind of burn will likely result in blistering and will take longer to heal
A third-degree burn is the most serious as it damages all layers of skin and often some of the tissue below. These kinds of burns will likely require skin grafts to heal properly
Types
Apart from degrees, there are also several types of burns. These include:
- Thermal – These are the most common type of burns and occur when the skin comes into contact with a heat source, like boiling water, open flames, or hot metal
- Chemical – These occur when the skin or eyes come into contact with an irritant, like an acid. Inhaling certain chemicals can also result in chemical burns.
- Electrical – These happen when high-voltage electricity passes through the body and damages tissues.
- Radiation—This can be either internal or external. Internal radiation burns happen when radioactive materials are ingested, while external radiation burns come from exposure to ultraviolet rays.
What Happens To People When They Experience Extreme Burns?
The human body is mostly water—about 60%. When we experience a burn, this water starts to evaporate quickly, which in turn causes further damage to the skin and underlying tissue.
Damage of Degree Burns
As mentioned before, first-degree burns only damage the epidermis, so there isn’t much to worry about other than some redness, swelling, and pain.
Second-degree burns are more severe as they damage the epidermis and dermis. This layer of skin is where we have our sweat glands, hair follicles, and blood vessels. When this layer is damaged, it can cause blistering, deep redness, and severe pain.
Third-degree burns are the most serious, as they damage all skin layers and some of the tissue below. To heal properly, these kinds of burns will likely require skin grafts.
Inhalation Burns
Inhalation injuries are also hazardous, as they can damage the lungs. Hot gases can cause swelling and fluid build-up in the lungs, making breathing difficult.
Extreme Heat can also lead to shock when the body cannot pump enough blood to the vital organs. This can cause organ damage and even death.
Extreme Burns and Our Bodies
Now that we know more about extreme burns let’s examine them more to see how they affect our bodies.
What Temperature Does the Human Body Burn At?
The human body can start to experience burns at around 43 degrees Celsius, while the average body temperature is 37 degrees Celsius.
The skin’s proteins denature at this temperature, changing shape and structure.
Xem thêm : What Causes Goosebumps?
This change in structure leads to further damage as the proteins can no longer perform their normal functions.
This would also mean that more negative effects can be expected if the temperature rises.
Could Skin Melt if it Was Hot Enough?
Yes, skin can melt if it is exposed to high enough temperatures.
However, it would take an extremely high temperature for this to happen
For example, a study found that it would take a temperature of approximately 700 degrees Celsius to melt human skin! Fortunately, there are very natural phenomena that cause this to happen.
One of these can be found when a volcano erupts. The flow from these volcanoes can reach these deadly temperatures.
At What Temperature Can Hot Water Instantly Burn Skin Off?
Hot water can cause severe burns if the temperature is high enough.
For example, water at 60 degrees Celsius can cause a third-degree burn in just five seconds!
This is because the proteins in the skin start to denature and break down at this temperature.
This means the hot water doesn’t take long to cause severe damage.
At What Temperature Would Fats Start to Melt?
The answer for fats is quite interesting. It is mainly dependent on where fats are located within the body.
For instance, visceral fat – or fat hidden within a person’s body – would take anywhere from 30 to 35 degrees Celsius. While this isn’t as hot as other extreme heat points we’ve discussed, we are currently covering the effects of exercise and burning to that. This also relates to surgical procedures that aim to melt these fats.
What Temperature Would You Have to be Exposed To To Die?
There is no one answer to this question, as it depends on several factors.
For example, if you have a higher body fat percentage, you can withstand higher temperatures than someone with less body fat.
That being said, exposure to temperatures above 70 degrees Celsius can be deadly.
The body starts to shut down at this temperature, and vital organs fail.
Of course, there are always exceptions to the rule, and some people have been known to survive temperatures as high as 45 degrees Celsius.
Hottest Temperatures People Can Withstand
As mentioned previously, the hotter it gets, the worse it gets for people. Despite that, people do exhibit resilience towards heat. That said, though, there is a limit. So, what are the hottest temperatures people can withstand?
According to a 2020 study, the highest temperature people can survive is around 35 degrees Celsius. Some may wonder why this temperature is lower than the average human body temperature. This is because the experiences outside and inside the body are different.
With that said, though, certain factors need to fall into place.
Humidity as a Factor
Even at 35 degrees Celsius, the body won’t be pushed to its limits if the humidity is low. Extreme heat researchers state humidity is a significant factor in people’s survival. This means that temperature and humidity must be pretty high to be dangerous.
This deadly combination hampers the body’s ability to regulate its internal temperature. People can sweat, but the cooling system won’t keep up.
Xem thêm : Bacon Quarter Pounder®* with Cheese
When this happens, the body will not immediately give out. It can take up to three hours to kill a person.
What Is The Hottest Temperature Ever Recorded?
The hottest recorded temperature was on 13 September 1922 in El Azizia, Libya. The mercury hit a whopping 56.7 degrees Celsius!
Interestingly, this record has been disputed recently, as some believe the instruments used were inaccurate.
Regardless, it’s safe to say that temperatures above 50 degrees Celsius are infrequent and dangerous.
Despite that, hyperthermia occurs once body temperatures reach 40 degrees, and it has its symptoms. Let’s learn more about this condition.
On Hyperthermia
Hyperthermia is caused by extreme heat. It occurs when a person’s core temperature reaches 37.5 to 38.3 degrees Celsius. In layman’s terms, this condition occurs when a person’s core body temperature reaches high levels.
Hyperthermia can manifest in many forms or types.
Hyperthermia Types
Cramps
The first form of hyperthermia is heat cramps. These cramps affect body parts like the arms or legs and directly result from the heat, making a person sweat and lose the required electrolytes.
Exhaustion
Next up is exhaustion. Once it gets too hot, people experience a wave of exhaustion. They feel exhausted; if left untreated or unchecked, it can have fatal consequences.
Rashes
The third form is rashes. The high heat makes a person’s skin react, leaving blisters or rash clusters in an area. These usually occur in body parts that rub together or are obscured, like neck folds, under breasts, or in the groin area.
Stress
This next one occurs more in people who work in hotter conditions. These include construction workers, firemen, or anyone who works under the sun. While not as severe as the others, it can directly lead to heat exhaustion.
Stroke
The final type is heatstroke, which is considered the worst type. At this stage, the body’s overloading temperature can directly affect a person’s brain and vital organs needed to survive.
Hyperthermia Symptoms
Apart from these types, several symptoms manifest in people experiencing hyperthermia. These include:
- fatigue;
- headaches;
- increased heart rates;
- lower blood pressure;
- vomiting; and
- general weakness
Fortunately, all these symptoms and types can be avoided or treated by following the proper steps.
Treating Hyperthermia
Treating heat cramps, stress, exhaustion, and rashes is pretty simple. These are considered very mild symptoms and can be easily managed with the following steps.
- Stopping any activity and resting in a calm and shaded area.
- Stretching out any cramps and drinking water.
- Letting the body air out by removing any hot clothing.
- Replacing electrolytes within the body by drinking sports drinks.
- Not drinking caffeinated drinks.
- Placing cold compresses on infected rash areas or hot parts of the skin.
- Managing irritation of the skin by keeping the affected area dry.
These are only simple treatments for the first four types, though. Heatstroke is very serious and an entirely different thing.
Treating Heatstroke
With heatstroke as severe and fatal as it is, the first thing that should be done is to always get to a hospital immediately. Once there, treatment can be offered.
However, it is possible that when waiting for transportation like an ambulance, the effects of heatstroke can take over. When that happens, follow these simple steps:
- Introduce cold water to people by immersing them in a tub or spraying it on their body
- Create or take ice packs and place them on the neck and groin areas
- Do not take any medications, such as aspirin. These may serve to worsen any symptoms
At the hospital, though, patients will likely need cold IV fluids to help cool the body.
Calm and Cool
The effects of extreme burns and extreme heat on the human body are numerous, with potentially deadly consequences. The good thing is that we’ve learned a lot about these extreme temperatures and their effects on the body.
The one thing we can see from all this is that these conditions and effects are easily preventable. All one needs to do is use this information to stay calm and relaxed.
Supplement all this knowledge with the proper burn first aid practices, which will help treat and prevent heat-related conditions.
Learn more about it through CPR First Aid’s Liverpool course today.
Subscribe now & receive Exclusive DISCOUNTS on your booking!
Nguồn: https://blogtinhoc.edu.vn
Danh mục: Info
This post was last modified on Tháng mười một 20, 2024 2:31 sáng